What is Cloning?
1. Who is Dolly?
The first cloned lamb.
2. When a zygote divides into to separate cells, it is called:genetically identical twins.
3. Somatic cells are also called diploid.
4. In order to clone a gene, a gene is inserted into a plasmid.
5. In order to create an embryo from a somatic cell, the donor egg cell must have its nucleus removed.
Click and Clone
6. List all the materials needed to clone a mouse.
Microscope
Sharp Pipette
Blunt Pipette
Petri Dish
Chemical to simulate cell division
7. Place the following steps in the correct order.
4. Stimulate cell division
6. Deliver baby
2. Remove and discard the nucleus from the egg cell
1. Isolate donor cells from egg donor and germ cell donor
3. Transfer the somatic cell nucleus into the egg cell
5.Implant embryo into a surrogate mother
8. There are two time gaps in the process of cloning. What are they? (ie. what do you have to wait for?)
1. The DNA needs to be rebooted to program as though it were an egg cell.
2. The cell needs to divide a few times.
9. What color with the cloned mouse be? What is the name of this mouse?
Brown, Mini-Mimi
Why Clone?
10. Why is cloning extinct animals problematic?
They find trouble, however, when they realize that the cloned creatures are smarter and fiercer than expected.
11. What are some reasons a person might want to clone a human?
To replace a deceased child and to help infertile couples have children
The Clone Zone
12. What animal was cloned in 1885?
Sea urchins
13. How did Spemann separate the two cells of the embryo of a salamander in 1902?
The hair of a baby and split the to cells.
14. The process of removing a nucleus is called enucleation.
15. In 1952, the nucleus of a frog embryo cell was placed into a donor cell. Did it work to clone the animal?
Some worked and some did not.
16. Can the nucleus of an adult cell be injected into an egg cell and produce a clone?
No
17. Why are mammals hard to clone?
The egg cells are smaller.
18. What were the names of the first two cloned cows?
Prather and Eyestone
19. In what year was the National Bioethics Advisory Council formed?
1997
20. The first mammal clone to be produced from an adult (somatic) cell?
Dolly the lamb
21. What do scientists do to adult cells to make them "behave" like embryos?
They give them a little electric shock
22. Transgenic, cloned sheep were used to produce what medical protein?
Factor IX
23. What is a stem cell?
They are found in organisms and they get their name from their ability to grow themselves again through mitotic cell division.
Cloning Myths
24. Briefly describe in your own words, why CC the cat was not identical in color to Rainbow, even though she was a clone?
CC looks different because Rainbow had different genes turned on and off on her X chromosome. Since CC had different genes on and off than Rainbow, the outcome of fur color was different.
25. What is "nature vs nurture"?
It is the thought that nature shapes you more than how you are raised. Different people believe different things about this such as one person could believe that you are who you are by who you were raised to be, and another person can say life experiences shape you personality and how you were raised doesn't do anything. I believe both are true, how we are raised and our life experiences shape who we become.
Is it Cloning or Not?
26. For each of the following scenarios, indicate YES (it is cloning) or NO (it is not cloning)
NO Sperm taken from a mole goat is combined with a female's egg in a petri dish. The resulting embryo is implanted into the female's uterus to develop
YES A sheep embryo, composed of 16 cells, is removed from the mother's uterus and separated into individual cells. Each cell is allowed to multiply, creating 16 separate embryos, which are then implanted in different female sheep to develop to maturity.
NO A cow with many desirable traits is stimulated with hormones to produce a number of egg cells. Each of these eggs is fertilized and implanted into a surrogate mother.
NO In vitro fertilization
YES Cell nuclei from an extinct wolly mammoth are placed into enucleated cow cells.
27. Define or describe each of the following processes (you may need to reset the Cloning or Not Screen)
In Vitro fertilization- The process by which sperm is used from outside sources to impregnate a woman that has had difficulty getting pregnant
Embryo splitting-The cells in the embryo are taken out and therefore creating clones of the original.
Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer-The process by which scientists clone the embryo of an animal.
Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer-Nuclei and egg cells are combined to make clones or the original.
Artificial Insemination-Sperm is placed into the egg cells to fertilize the cells, but it is not cloning.
What Are the Risks of Cloning?
28. What is one reason why cloning animals has such a high failure rate?
The implanting of the embryo into the surrogate mother could possibly fail.
29. What is a telomere and how does it affect cloned animals?
Telomeres are the ends of the DNA strand in the cells, and that effects cloned animals because if the telomeres are shorter then it means that the DNA is aging quickly or the animal is or was old.
What Are Some Issues in Cloning?
30. Pick one of the questions to ponder and ....ponder it. Write a brief essay on your thoughts and opinions.
What are some of the social challenges a cloned child might face?
Some challenges that a cloned child might face is that if the child has any differences than the other kids because something went wrong during the cloning process or that the child looked exactly like the other so they could not do things that the other original could do because the original had already done the stuff such as get a drivers license or go to the same college. Also the child would not get as much attention because he is just a duplicate and no one really appreciates that he is there.
Another challenges that the clone might face is that the original might want to take advantage of the clone such as make the clone take the blame for stuff, or go to detention for the original, or just do the dirty work. That is not fair to the child because he is his own person even if he was created from another human. He has every right that the original has just they look exactly the same.
Lastly, another possibility is that the child we would get some much attention because he is a clone that he could get overwhelmed and people could get jealous of him and he could get some people that are fed up with him getting all the attention such as the original person. They could humiliate him or harass him because they just don't like him and that would make a difficult life for a clone because he was created, not born like a normal human being and he is just trying to fit in with society and people are giving him a hard time.
Genetics Reflection
Monday, January 3, 2011
Thursday, December 16, 2010
Harvest Of Fear
Should we Grow GM Crops?
Instructions: Read the page and click YES or NO, reach the next...click YES or NO...etc until you’ve read all the arguments -- You will need to do this 12 times in order for your votes to be tallied. Navigate the site, each of the bold headings below are links within the site
1. What is a GM Crop.
A genetically modified crop.
2. List 2 arguments FOR the growing of GM crops
a. GM foods will have even greater benefits for the world's poor, supporters state. With genetically modified foods, simple foods like rice and such can give you all the nutrition you need. For developing countries, if rice is all they can afford, this "golden rice" can give them all the nutrition they need.
b. Genetic modification couldn't be more natural. When mixing genes and putting them into another organism, you are not disrupting the circle of life because the basis of evolution is that they would have done it anyway. We are just speeding up the process.
3. List 2 arguments AGAINST the growing of GM crops.
a. Even if farmers in developing countries don't grow GM crops, they could still be hurt by them. Although these farmers are not influenced directly, they are still effected because when people see the new improved foods with high nutrition, they will not buy from the smaller farmers and they will go out of business.
b. One of their greatest worries is that GM crops could harm other wildlife. The GM plants may be hurting/killing other organisms because they cannot either adapt to the change in the other organism, or the organism is giving off a new substance that hurts/kills the other plant.
*Read some of the reader’s responses.
Engineer a Crop
4. Practice this simulation until you get the largest ears of corn. How many times did it take you?
It took me one time.
What’s for Dinner?
*Click on the foods on the table to see what research is being done to bioenginner the foods.
5. List two foods and desribe how they are being modified.
Sushi- Researchers are trying to genetically modify rice with altered starch levels, pest resistant, and "edible nutrition". Salmon might also become the first GM fish.
Fries- Potatoes are engineered to absorb less of the oil they are fried in. Bioengineers are also trying to generate a better oil to fry the fries in the make them healthier with fwer saturated fats.
Viewpoints
*Read the article titled “Are GM Food Sufficiently Regulated in the US?”
Do you think food should be labeled if it has been genetically modified? Why or Why not?
Yes I do think that foods should be labeled if they are genetically modified or not because people need to know what they are eating. If the manufactures injected peanut oil into some foods because it made the food taste better, or for whatever reason, they need to know if they can eat that food. If the manufactures had put peanut oil into some random food such as apples because it made them juicier, then a person with peanut allergies needs to jnow before they wind up at the hospital.
Finished? Go to www.yahooligans.com and type "genetic engineering" in the search field. Browse some of the sites that pop up.
(Yahooligans is better than yahoo, the sites tend to be picked for education rather than for scientists and universities, you'll find more understandable and interesting sites on yahooligans than you will with Yahoo)
Write down any of the sites you visited below.
http://www.eurekascience.com/ICanDoThat/cloning_pt.htmhttp://www.eco-pros.com/geewhizfood.htm
http://www.eco-pros.com/genetic_engineering.htm
Instructions: Read the page and click YES or NO, reach the next...click YES or NO...etc until you’ve read all the arguments -- You will need to do this 12 times in order for your votes to be tallied. Navigate the site, each of the bold headings below are links within the site
1. What is a GM Crop.
A genetically modified crop.
2. List 2 arguments FOR the growing of GM crops
a. GM foods will have even greater benefits for the world's poor, supporters state. With genetically modified foods, simple foods like rice and such can give you all the nutrition you need. For developing countries, if rice is all they can afford, this "golden rice" can give them all the nutrition they need.
b. Genetic modification couldn't be more natural. When mixing genes and putting them into another organism, you are not disrupting the circle of life because the basis of evolution is that they would have done it anyway. We are just speeding up the process.
3. List 2 arguments AGAINST the growing of GM crops.
a. Even if farmers in developing countries don't grow GM crops, they could still be hurt by them. Although these farmers are not influenced directly, they are still effected because when people see the new improved foods with high nutrition, they will not buy from the smaller farmers and they will go out of business.
b. One of their greatest worries is that GM crops could harm other wildlife. The GM plants may be hurting/killing other organisms because they cannot either adapt to the change in the other organism, or the organism is giving off a new substance that hurts/kills the other plant.
*Read some of the reader’s responses.
Engineer a Crop
4. Practice this simulation until you get the largest ears of corn. How many times did it take you?
It took me one time.
What’s for Dinner?
*Click on the foods on the table to see what research is being done to bioenginner the foods.
5. List two foods and desribe how they are being modified.
Sushi- Researchers are trying to genetically modify rice with altered starch levels, pest resistant, and "edible nutrition". Salmon might also become the first GM fish.
Viewpoints
*Read the article titled “Are GM Food Sufficiently Regulated in the US?”
Do you think food should be labeled if it has been genetically modified? Why or Why not?
Yes I do think that foods should be labeled if they are genetically modified or not because people need to know what they are eating. If the manufactures injected peanut oil into some foods because it made the food taste better, or for whatever reason, they need to know if they can eat that food. If the manufactures had put peanut oil into some random food such as apples because it made them juicier, then a person with peanut allergies needs to jnow before they wind up at the hospital.
Finished? Go to www.yahooligans.com and type "genetic engineering" in the search field. Browse some of the sites that pop up.
(Yahooligans is better than yahoo, the sites tend to be picked for education rather than for scientists and universities, you'll find more understandable and interesting sites on yahooligans than you will with Yahoo)
Write down any of the sites you visited below.
http://www.eurekascience.com/ICanDoThat/cloning_pt.htmhttp://www.eco-pros.com/geewhizfood.htm
http://www.eco-pros.com/genetic_engineering.htm
Monday, December 6, 2010
Epigenome
Identical twins
Identical twins become different over time because of environmental factors. This are the factors that shape the epigenome. From experiences and choices in their life, identical twins develop a different epigenome and therefore form a different phenotype.
A couple of factors that shape the epigenome are diet, stress, and different activities the twins choose throughout their life.
An imprinted gene is a gene that gives you traits from your parents epigenome. The epigenome tags on your genome are imprinted onto your epigenome from your parents.
Factors in my life that are shaping my genome are the decisions I make, the games I play, the people I meet, the people I follow, the people I learn from, everyone around me, and everything everyone does around me.
Lick your rats
High nurtured rats create more GR genes therefore giving the rat the ability the quickly get over stress because the cortisols attach to the GR genes and there not as many just floating around giving the highly nurtured rat the ability to get over stress easier.
The licking of the rat from a mother activates the GR genes.
The cortisols and the GR genes work together in order to give the organism the ability to either get rid of stress easily or difficultly from either high amount or low amount of GR genes.
Parents have a big impact on their children because they are the people they look up to. What the parent does or says, is effecting the child's actions. If a parent is loving and caring to that child, then he/she will most likely grow up to be a caring, loving parent. On the other hand, if the parent is abusive, then the child will grow up and most likely make the wrong decisions and become a mean, abusive parent.
Nutrition and The Epigenome
The food we eat can effect our epigenome because of the chemicals in the food. Those chemicals can effect the body in different ways. If one organism cannot withstand the effects of that chemical, then the body may act in a negative way. Whereas if the body can tolerate the chemical, then it may have a positive effect or not one at all.
Yes the diet of the mother can effect the offspring while the offspring is still in the fetus because whatever the mother eats, the nutrition goes through the umbilical cord and into the offspring. The nutrition of the food can effect the babies epigenome.
Epigenetics and the Human Brain
The methyl can influences the gene expression because the DNA methylation stabilizes the gene expression, which is important for storing information for a long time.
Drugs of abuse such as cocaine trigger epigenetic changes in certain brain regions, affecting hundreds of genes at a time. Some of these changes remain long after the drug has been cleared from the system. Research in this area suggests that some of the long-term effects of drug abuse and addiction may be written in epigenetic code.
Identical twins become different over time because of environmental factors. This are the factors that shape the epigenome. From experiences and choices in their life, identical twins develop a different epigenome and therefore form a different phenotype.
A couple of factors that shape the epigenome are diet, stress, and different activities the twins choose throughout their life.
An imprinted gene is a gene that gives you traits from your parents epigenome. The epigenome tags on your genome are imprinted onto your epigenome from your parents.
Factors in my life that are shaping my genome are the decisions I make, the games I play, the people I meet, the people I follow, the people I learn from, everyone around me, and everything everyone does around me.
Lick your rats
High nurtured rats create more GR genes therefore giving the rat the ability the quickly get over stress because the cortisols attach to the GR genes and there not as many just floating around giving the highly nurtured rat the ability to get over stress easier.
The licking of the rat from a mother activates the GR genes.
The cortisols and the GR genes work together in order to give the organism the ability to either get rid of stress easily or difficultly from either high amount or low amount of GR genes.
Parents have a big impact on their children because they are the people they look up to. What the parent does or says, is effecting the child's actions. If a parent is loving and caring to that child, then he/she will most likely grow up to be a caring, loving parent. On the other hand, if the parent is abusive, then the child will grow up and most likely make the wrong decisions and become a mean, abusive parent.
Nutrition and The Epigenome
The food we eat can effect our epigenome because of the chemicals in the food. Those chemicals can effect the body in different ways. If one organism cannot withstand the effects of that chemical, then the body may act in a negative way. Whereas if the body can tolerate the chemical, then it may have a positive effect or not one at all.
Yes the diet of the mother can effect the offspring while the offspring is still in the fetus because whatever the mother eats, the nutrition goes through the umbilical cord and into the offspring. The nutrition of the food can effect the babies epigenome.
Epigenetics and the Human Brain
The methyl can influences the gene expression because the DNA methylation stabilizes the gene expression, which is important for storing information for a long time.
Drugs of abuse such as cocaine trigger epigenetic changes in certain brain regions, affecting hundreds of genes at a time. Some of these changes remain long after the drug has been cleared from the system. Research in this area suggests that some of the long-term effects of drug abuse and addiction may be written in epigenetic code.
Tuesday, November 23, 2010
DNA Fingerprinting
Introduction:
1. DNA is unique for everyone. The only exception is if a person has what?
1. DNA is unique for everyone. The only exception is if a person has what?
An Identical Twin
2. What are DNA fingerprints used for?
2. What are DNA fingerprints used for?
DNA fingerprints can be used for anything from determining a biological mother or father to identifying the suspect of a crime
Part 1 “It Takes a Lickin”
3. What “crime” was committed?
Part 1 “It Takes a Lickin”
3. What “crime” was committed?
Someone licked Jimmy Sweet’s holographic NOVA lollipop.
4. What bodily fluid was removed from the “crime scene” to get DNA?
4. What bodily fluid was removed from the “crime scene” to get DNA?
Saliva
Part 2 “DNA Fingerprinting at the NOVA Lab”
5. What does a restriction enzyme do?
Part 2 “DNA Fingerprinting at the NOVA Lab”
5. What does a restriction enzyme do?
Cuts that long DNA molecules at different locations.
6. What is agarose gel?
6. What is agarose gel?
A thick, porous, Jello-like substance. It will act like a molecular strainer.
7. What is electrophoresis?
The process of moving molecules with an electric current
11. Which chemical in your “virtual lab” is radioactive?
The probes.
8. Smaller fragments of DNA move ____________ than longer strands?
Farther toward the tray’s opposite end
9. Why do you need to place a nylon membrane over the gel?
9. Why do you need to place a nylon membrane over the gel?
Because the agarose gel is difficult to work with. The DNA transferred to a nylon membrane.
10. Probes attach themselves to __________
10. Probes attach themselves to __________
DNA fragments on the nylon membrane.
12. Sketch your DNA fingerprint. 11. Which chemical in your “virtual lab” is radioactive?
The probes.
13. Based on your DNA fingerprint, who licked the lollipop?Honey
Click on the Link “DNA Workshop” (if this link won't load, scroll down to the bottom where it says "try the non-java script version)
Once you’re there, go to the link “DNA Workshop Activity” and practice with DNA replication and protein synthesis.
Browse the DNA Workshop site.
14. What kinds of things could you do at the DNA workshop?
Once you’re there, go to the link “DNA Workshop Activity” and practice with DNA replication and protein synthesis.
Browse the DNA Workshop site.
14. What kinds of things could you do at the DNA workshop?
Copy the DNA and make the codons and the proteins from the codons.
Find an Article about DNA
15. Read an article about genetics at this site that you might find interesting, or use the "Search" box in the upper right hand corner to search for DNA fingerprinting.
Title of Article DNA double-strand break signaling and human disorders
Author and Date Toshiyuki Bohgaki , Miyuki Bohgaki and Razqallah Hakem November 5, 2010
Author and Date Toshiyuki Bohgaki , Miyuki Bohgaki and Razqallah Hakem November 5, 2010
Summarize what the article was about. Write this in a paragraph format.
This article was about how DNA double-strand breaks are the most serious type of DNA damage. This repair from these breaks are vital for organisms such as humans and animals to survive. The repair of DNA breaks are fundamental as demonstrated by the many human syndromes, neurodegenerative diseases, immunodeficiency and cancer. Homologous recombination and non-homologous end-joining pathways are the two major DNA repair pathways that mediate the repair of DNA double-strand breaks.
Wednesday, November 3, 2010
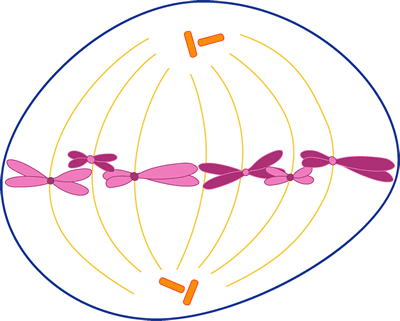
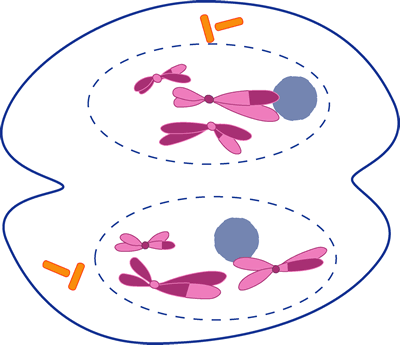
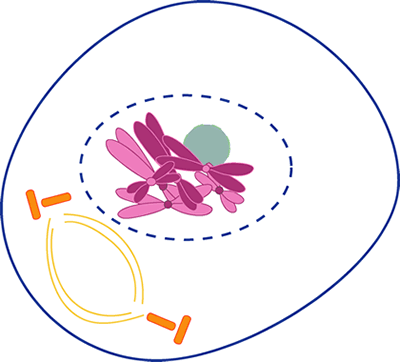
Mitosis
1. Which stage does chromatin condense into chromosomes?
Prophase
Which stage does chromosomes align in the center of the cell?
Metaphase
Which stage is the longest past of the cell cycle?
Interphase
Which stage does the nuclear envelope break down?
Prometaphase
Which stage does the cell cleave into two new daughter cells?
Anaphase
Which stage do daughter chromosomes arrive at the poles?
Telophase
Prophase
Which stage does chromosomes align in the center of the cell?
Metaphase
Which stage is the longest past of the cell cycle?
Interphase
Which stage does the nuclear envelope break down?
Prometaphase
Which stage does the cell cleave into two new daughter cells?
Anaphase
Which stage do daughter chromosomes arrive at the poles?
Telophase
2. The colored chromosomes represent chromatids. There are two of each color because one is an exact duplicate of the other.
--How many chromosomes are visible at the beginning of mitosis? 8
-- How many are in each daughter cell at the end of mitosis? 4
--The little green T shaped things on the cell are: Centrioles
-- What happens to the centrioles during mitosis? They move to opposite sides of the cell
3. Identify the stages of these cells:
Prometaphase Cytokinesis Prophase
View the animation and sketch the cell in:
The centrioles move to opposite sides of the cell.
Spindle fibers attach to chromosomes.
The cell splits into two daughter cells.
You will have 36 cells to classify. When you’re finished, record your data in the chart below.
Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Total Number of cells 20 10 3 2 1 36 Percent of cells
(calculate: number of cells divided by total cells x 100 )
56% 28% 8% 5% 3% 100 %
View 1 | View 2 | View 3 | View 4 | View 5 | |
| Whitefish | Telophase | Metaphase | Prometaphase | Anaphase | |
| Onion | Metaphase | Prometaphase | Interphase | Interphase | Telophase |
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)